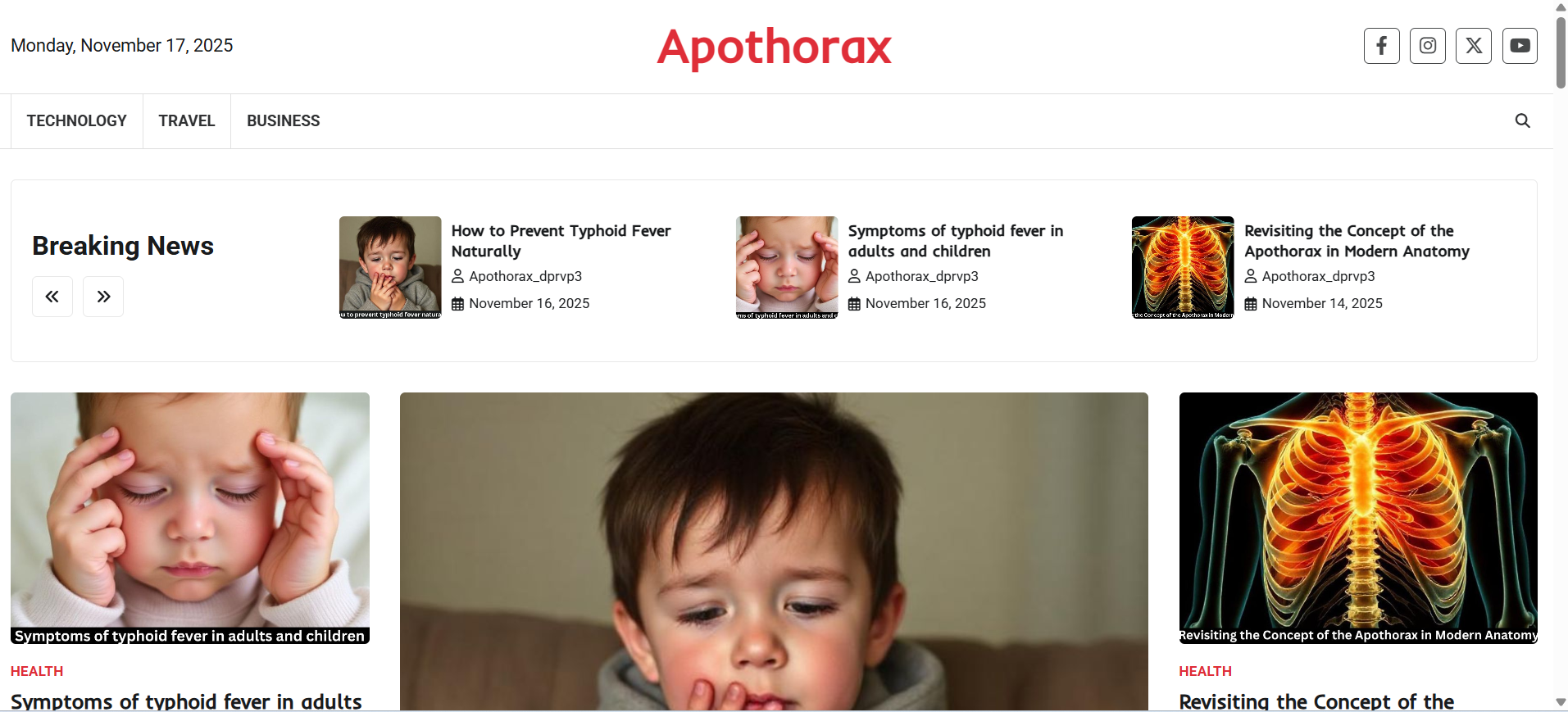
Studying anatomy often means learning terms that aren’t always used in modern textbooks—and the apothorax is one of them. Yet the region is still useful for understanding how the chest wall supports breathing and protects vital organs. This quick revision guide breaks it down in the simplest way possible.
Why the Apothorax Confuses Students
Because it sounds like a formal anatomical cavity, many assume the apothorax holds organs. But it’s actually a supportive region, not a cavity.
Importance of Understanding This Region
Knowing the apothorax helps you better visualize the layers surrounding the thorax and how they work together.
What Is the Apothorax?
Simple Definition
The apothorax refers to the supportive area around the thorax, especially the lower side regions of the chest wall.
Etymology and Meaning
- “Apo” = around / supporting
- “Thorax” = the chest
So apothorax literally means “around the thorax.”
Why It’s Not Commonly Used Today
Modern anatomy uses more specific terms for the muscles, bones, and tissues in this region. However, the concept is still valuable.
Location of the Apothorax
Anatomical Position
The apothorax is located:
- On the lower lateral sides of the chest
- Near the upper abdominal wall
- Surrounding the lower ribcage
Boundaries of the Region
Although informal, it typically includes:
- Ribs 8–12
- Lower intercostal spaces
- Costal cartilages
- Upper diaphragm attachments
Connection With the Thorax and Abdomen
It forms a transition zone that stabilizes the chest and assists movement of the diaphragm.
Structures Found in the Apothorax
Muscles
Key muscles include:
- External and internal intercostals
- Serratus anterior
- External oblique
- Parts of transversus thoracis
Bones & Cartilage
The region contains:
- Lower ribs
- Costal cartilages
- Segments of thoracic vertebrae
Nerves, Vessels & Connective Tissues
It houses:
- Intercostal nerves
- Thoracic spinal nerves
- Intercostal arteries & veins
- Lymphatic vessels
- Connective tissue layers
Function of the Apothorax
Supportive Role
The apothorax strengthens the chest wall and provides structural support for breathing.
Contribution to Breathing
Its muscles:
- Lift and lower the ribs
- Assist the diaphragm
- Maintain chest wall flexibility
Importance in Posture & Movement
The region supports:
- Lateral bending
- Trunk rotation
- Core stabilization
Why the Apothorax Matters in Anatomy
Link to Thoracic Protection
Though not a cavity, the apothorax reinforces the chest wall that protects organs like:
- The heart
- The lungs
- Major vessels
Helps Stabilize Rib Cage
It keeps ribs aligned and functioning properly during breathing.
Supports Lung and Diaphragm Function
The apothorax ensures the lungs expand smoothly and the diaphragm moves efficiently.
Apothorax vs. Thorax
Key Differences
- Thorax: A cavity containing organs.
- Apothorax: A supportive region around the thorax.
Functional Comparison
- Thorax: Manages breathing and circulation.
- Apothorax: Ensures ribcage stability and assists respiratory movement.
Why Understanding the Difference Helps Students
It prevents confusion and helps in learning thoracic wall anatomy.
Common Misconceptions About the Apothorax
Is It a Cavity?
No. It is not a hollow space or organ compartment.
Does It Contain Organs?
No. It contains supportive muscles, bones, and connective tissue.
Why Students Misinterpret It
The similarity to “thorax” leads many to think it’s a sub-region inside the chest cavity.
Quick Study Tips
Mnemonics
Try this:
“Apo supports the thorax.”
Short, simple, and perfect for revision.
Visual Learning
Use:
- Diagrams
- 3D anatomy apps
- Labeled charts
How to Remember Its Structure and Role
Think of the apothorax as the reinforcement layer protecting and stabilizing the thorax.
Conclusion
The apothorax may not be a mainstream term today, but it plays a major role in understanding thoracic support, breathing mechanics, and chest wall stability. Knowing this region helps students visualize how the ribs, muscles, and connective tissues work together to protect vital organs and support everyday movement.
FAQs
1. Does the apothorax contain organs?
No—it’s a supportive region, not a cavity.
2. Which ribs are part of the apothorax?
Generally ribs 8 to 12.
3. Why isn’t the term used in modern anatomy?
Modern anatomy prefers more precise terminology for structures in this region.
4. What is the main function of the apothorax?
To support breathing, stabilize the rib cage, and reinforce chest wall structure.
5. Is the apothorax important for exams?
Yes, especially for descriptive anatomy and comparative anatomy questions.